Fat isn't a diet enemy - this macronutrient is essential for maintaining good heart health, reducing inflammation, and maintaining optimal body function. Learn more about how to get your fill of vegan healthy fats from a variety of plant-based sources.
People completely misunderstood and underestimated fat for some time, believing that eating fat in their diet would cause weight gain.
This message is changing as high-fat diets like keto grow in popularity, and we recognize fat as what it truly is - a macronutrient that's crucial for a load of bodily functions. We cannot survive without eating fat, but not all fats are the same. Certain types of dietary fat are better than others, with better health benefits to reap from them.
With animal-based sources as a massive contributor to dietary fat intake, vegans who remove meat, dairy, eggs, and fish may wonder how they're going to consume a high-fat vegan diet.
There are plenty of plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids and healthy fat foods that are entirely plant-based so that vegans can reach their recommended daily intake of this vital macronutrient.
Read below to learn more about dietary fats, the importance of consuming healthy fats, and the best fatty vegan foods to keep your body and mind healthy.
What Are Fats?
We can break down all of the foods we eat into three macronutrients - fat, carbohydrates, and protein. We need all three in our diets, as they all perform different functions to keep our bodies running like well-oiled machines.
Fats, or fatty acids, are a three-molecule structure known as triglycerides. Our bodies create some triglycerides, but the body does not make some fat types, so we need to ingest them regularly to support bodily function. These fats are called "essential fats."
Essential Fats
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are the essential fats your body cannot create on its own. Omega-3's can be made to some degree by our bodies, but at a low rate, so the consumption of healthy fat sources is recommended to round out our essential fat intake.
Types of Fat
Not all fatty acids are created equal - there are three different types of fat we consume.
Saturated Fat
You do not need to avoid saturated fat altogether. Still, in larger doses, it can negatively affect your cholesterol levels and put you at a potentially higher risk for developing heart disease.
Most sources of saturated fats are animal-based, so it's easy to keep intake low while following a vegan diet. There are a couple of sources of vegan saturated fat, like coconut oil. Still, this plant-based saturated fat does not contribute to unhealthy cholesterol levels in the same way as animal sources do.
Unsaturated Fat
These are the MVP of the fat world and are considered the healthiest of the different fat types. There are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, both of which offer incredible health benefits.
Foods containing unsaturated fat can lower bad cholesterol, maintain crucial body cells, and have an antioxidative effect on the body.
Vegan foods high in fat tend to contain mostly unsaturated fat, primarily found exclusively in plant sources, like olive oil.
Trans Fat
Trans fats naturally occur in minimal amounts in some animal products. Artificial trans fats, on the other hand, are fats made by adding hydrogen to vegetable oil to solidify it. Trans fats are dangerous for our health, increasing bad cholesterol and heart disease risks.
The FDA currently bans trans fats in American food products.
What are Healthy Fats?
As we now know, not all of the fat types are healthy fats. Here's an ideal breakdown of a vegan's dietary fat intake:
- Never eat artificial trans fats, and keep natural trans fats to a minimum.
- Eat saturated fat in moderation, with less than 10% of your daily caloric intake from this type of fat.
- The rest of your fat intake should come from monounsaturated and polyunsaturated sources.
There are plenty of pros and cons to being a vegetarian; a whole, plant-based diet is already naturally lower in saturated fats, mostly from animals. Vegans will have an easier time balancing their fat levels by concentrating on including high-calorie vegan foods to increase unsaturated fats.
Why Do We Need Fats?
Dietary fat helps support many of our bodies' functions. Here are a few of the most important reasons to consume healthy fat:
- Provides energy and supports cell growth
- Lowers bad cholesterol and raises good cholesterol
- Reduces the potential risk of heart disease and inflammation
- Helps regulate blood pressure and blood clotting
- Supports brain development, mental health, and the maintenance of skin, hair, and nails
How Much Fat Do We Need?
The recommended intake for dietary fat isn't a specific, measured amount but a proportion of the calories you eat.
Adults should aim to eat 20-35% of their daily macronutrients in the form of dietary fats. While at most 10% of your total intake can be saturated fats, you should aim for at least 10-15% of your food intake coming from unsaturated fat sources to ensure optimal body function.
Healthy Vegan Fats: Plant-Based Sources
Plant-based omegas and unsaturated fats are easier to find than you might think. Here is a list of the tastiest plant-based fat sources that will keep you satiated and benefit your body.
Avocado
Avocados are some of the best high fat vegetables out there. They are also high in gut-healthy fiber, weighing in at 21 grams and 9 grams, respectively. They contain monounsaturated fat and a ton of oleic acid, which reduces heart disease risks, lowers bad cholesterol, and increases good cholesterol.
This nutrient-dense superfood is delicious in fresh guacamole, sliced on toast with a drizzle of olive oil, and even mashed with cocoa and maple syrup for a sweetly decadent vegan chocolate mousse.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are many of the most nutrient-dense foods available to us, not only for their high healthy fat content but also for protein and fiber, which helps keep your gut functioning well.
Walnuts are a great plant-based source for essential omega-3 fatty acids, and chia seeds have high levels of calcium, potassium, magnesium, and added prebiotic benefits to help your digestion even further.
Nut butter is an excellent source of added fats in a vegan diet. Your best choice is natural nut butter that doesn't contain added sugars.
Eat a handful of your favorite nuts or seeds, slather your toast in nut butter, or make pudding out of chia seeds to increase your healthy fat intake.
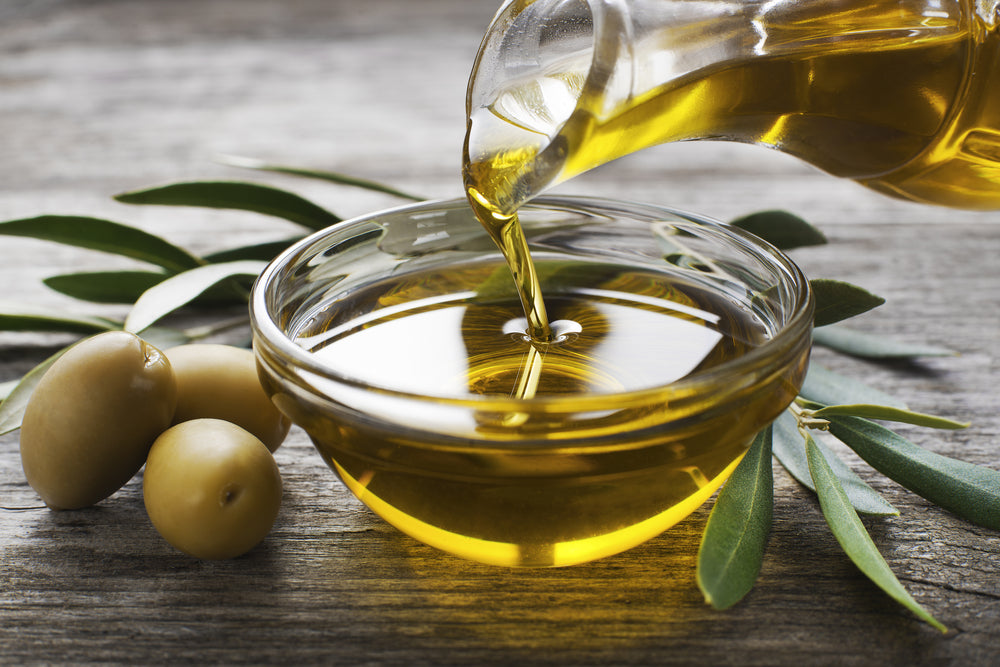
Olive and Coconut Oil
Olive and coconut oils are both high-calorie, healthy fast food that can be used in moderation to up your unsaturated fat intake.
Both oils have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effects on the body, and coconut oil contains lauric acid, helping lower cholesterol and aid weight loss.
Olive oil doesn't perform well under heat - it has a relatively low smoke point and releases toxic compounds when overheated. Use it as a drizzle on salads and other foods that don't need high heat. When you're cooking, opt for coconut oil, as it can withstand the high heat of the oven or stovetop without degrading.
Chocolate
Eating chocolate might be the tastiest way for vegans to increase their healthy fat consumption. The best chocolate to eat is pure cacao nibs, crumbled pieces of the cacao plant's dried beans.
Cacao is high in monounsaturated fat and antioxidants, so use these morsels in smoothies or baking. You can also eat a square or two of the darkest vegan chocolate bar you can find, which will contain the highest levels of cacao.
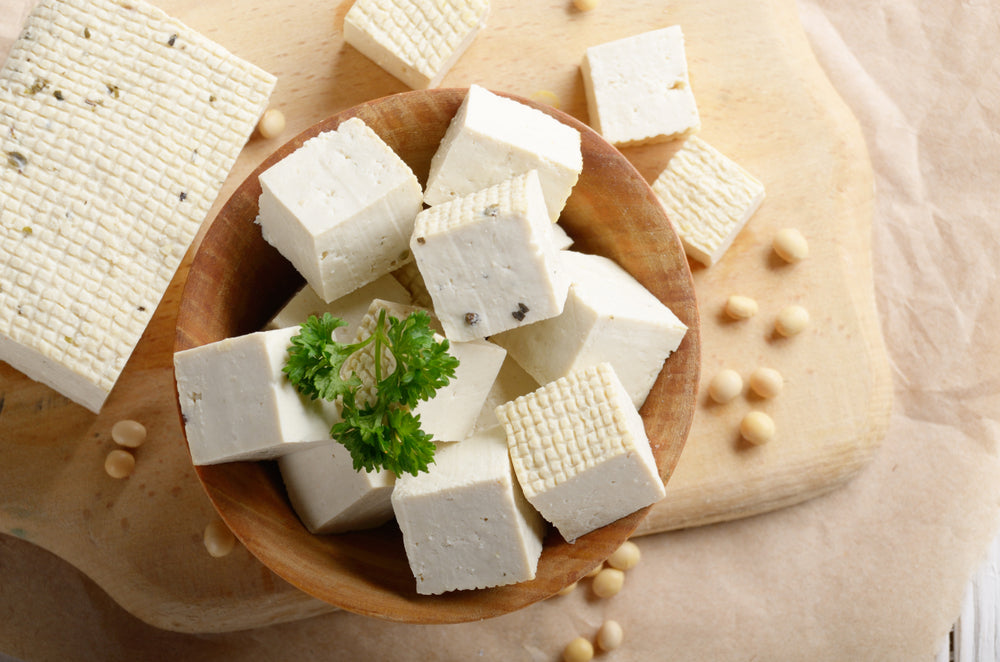
Tofu and Soybeans
Some of the vegan's best food options with healthy fats are soy-based. Soy is high in omega-3 fatty acids and a great source of other vitamins and minerals, like calcium and B vitamins.
All soy-based products, like tofu or soy milk, offer the same benefits as soybeans themselves, as well as a whack of plant-based protein, which is always helpful for vegan dieters.
Coconut
We've already mentioned coconut oil and its many impressively healthy properties. The rest of the coconut is full of nutrition, too, from full-fat coconut milk to flakes and coconut meat.
Capric and lauric acids support immune system function, and coconut products leave you feeling more satiated than other healthy fats, which aids weight loss.
Better yet, coconut in all forms tastes incredible and adds richness to curries and sweet dishes.
Final Notes: Healthy Fats for Vegans
There's no doubt that certain fats help our bodies to function optimally. Try to keep your vegan fat intake at 20-35% of your total food intake, and concentrate on including more unsaturated fat and less saturated fat.
Add a few of these nutrient-dense foods into your vegan diet regularly to keep your omega fatty acid levels up!







Leave a comment (all fields required)